
Note: A new GRASS GIS stable version has been released: GRASS GIS 7.6, available here.
Updated manual page: here
NAME
r.in.lidar - Creates a raster map from LAS LiDAR points using univariate statistics.KEYWORDS
raster, import, LIDAR, statistics, conversion, aggregation, binningSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -p
- Print LAS file info and exit
- -e
- Use the extent of the input for the raster extent
- Set internally computational region extents based on the point cloud
- -n
- Set computation region to match the new raster map
- Set computation region to match the 2D extent and resolution of the newly created new raster map
- -o
- Override projection check (use current location's projection)
- Assume that the dataset has same projection as the current location
- -s
- Scan data file for extent then exit
- -g
- In scan mode, print using shell script style
- -i
- Use intensity values rather than Z values
- Uses intensity values everywhere as if they would be Z coordinates
- -j
- Use Z values for filtering, but intensity values for statistics
- -d
- Use base raster resolution instead of computational region
- For getting values from base raster, use its actual resolution instead of computational region resolution
- -v
- Use only valid points
- Points invalid according to APSRS LAS specification will be filtered out
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name
- LAS input file
- LiDAR input files in LAS format (*.las or *.laz)
- output=name
- Name for output raster map
- file=name
- File containing names of LAS input files
- LiDAR input files in LAS format (*.las or *.laz)
- method=string
- Statistic to use for raster values
- Options: n, min, max, range, sum, mean, stddev, variance, coeff_var, median, percentile, skewness, trimmean
- Default: mean
- n: Number of points in cell
- min: Minimum value of point values in cell
- max: Maximum value of point values in cell
- range: Range of point values in cell
- sum: Sum of point values in cell
- mean: Mean (average) value of point values in cell
- stddev: Standard deviation of point values in cell
- variance: Variance of point values in cell
- coeff_var: Coefficient of variance of point values in cell
- median: Median value of point values in cell
- percentile: pth (nth) percentile of point values in cell
- skewness: Skewness of point values in cell
- trimmean: Trimmed mean of point values in cell
- type=string
- Type of raster map to be created
- Storage type for resultant raster map
- Options: CELL, FCELL, DCELL
- Default: FCELL
- CELL: Integer
- FCELL: Single precision floating point
- DCELL: Double precision floating point
- base_raster=name
- Subtract raster values from the Z coordinates
- The scale for Z is applied beforehand, the range filter for Z afterwards
- zrange=min,max
- Filter range for Z data (min,max)
- zscale=float
- Scale to apply to Z data
- Default: 1.0
- intensity_range=min,max
- Filter range for intensity values (min,max)
- intensity_scale=float
- Scale to apply to intensity values
- Default: 1.0
- percent=integer
- Percent of map to keep in memory
- Options: 1-100
- Default: 100
- pth=integer
- pth percentile of the values
- Options: 1-100
- trim=float
- Discard given percentage of the smallest and largest values
- Discard <trim> percent of the smallest and <trim> percent of the largest observations
- Options: 0-50
- resolution=float
- Output raster resolution
- return_filter=string
- Only import points of selected return type
- If not specified, all points are imported
- Options: first, last, mid
- class_filter=integer[,integer,...]
- Only import points of selected class(es)
- Input is comma separated integers. If not specified, all points are imported.
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
The r.in.lidar module loads LAS LiDAR point clouds into a new raster map using binning. The user may choose from a variety of statistical methods which will be used for binning when creating the new raster.Since a new raster map is created during the binning, the binning of points depends on the current computational region settings (extent and resolution) by default (see more about binning below). When using the -e flag, the binning will be done in the extent of the point cloud, so the resulting raster will have extent based on the input point cloud. When the resolution=value parameter is used, the binning is done using the provided resolution and the resulting raster will have that resolution (see more below for more information about extent and resolution management).
r.in.lidar is designed for processing massive point cloud datasets, for example raw LiDAR or sidescan sonar swath data. It has been tested with large datasets (see below for memory management notes).
Binning
The main different of r.in.lidar in comparison to r.in.lidar is that r.in.lidar creates a raster instead of just importing the points into GRASS GIS. However, r.in.lidar does not merely rasterizes the points from the point cloud. r.in.lidar uses binning to derive values for individual raster cells, so the value of a cell is typically an aggregation of values of individual points falling into one cell. In general binning is the conversion of points into a regular grid. The binning of points with X and Y coordinates starts with the overlay of a grid of bins over the points.In the basic case, binning is a method which counts the number of points which fall into one raster cell, i.e. bin. The number of points per cell (bin) indicates the density of points in the point cloud. The cell (bin) is always square or rectangular in case of r.in.lidar because the result is GRASS GIS 2D raster. The result of binning where the number of point per cell is counted is sometimes called 2D (two dimensional) histogram because a histogram is used in univariate statistics (in one dimension) to count the number samples falling into a given bin.
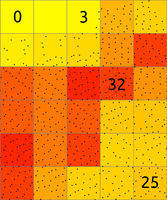
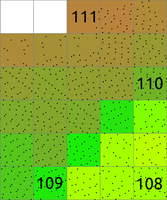
Figure: The binning on left was used to count number of points per (sometimes also called 2D histogram). The numbers in cells are examples of counts, the rest is represented by the color. The binning on right was used with mean to create a surface based on the values associated with the points. The numbers show examples of cell values. Note also the cells without any points which were assigned the NULL value.
Statistics
Available statistics for populating the output raster map are:- n
- This computes the number (count) of points per cell. The result is a indicator of spatially variable density of points in the given area.
- min
- This finds the minimum of point values in each cell. It can be useful when finding topography in a forested or urban environment and there is a lot of points per one cells (terrain is oversampled considering the desired resolution). It can also create surfaces independent on the noise from premature hits as it will always select the lowest point.
- max
- This finds the maximum of point values in each cell. In connection with base_raster it can yield maximum vegetation of feature height per cell. For this purpose, it is usually much more appropriate than mean which would yield heights mostly influenced by the vertical distribution of points.
- range
- This computes the range of point values in each cell. The range of Z coordinates per cell can be used as a rough estimate of vegetation height when the cells are small enough, slopes low and the area is mostly vegetated. However, for more profound analysis, the base raster together with different statistics is recommended.
- sum
- This computes the sum of point values per cell. This is useful especially when intensity is used as a value (flags -i and -j).
- mean
- This is a mean (average) value of point values in cell. When used with Z coordinates (the default) and points from the ground class, the resulting raster is a digital elevation model. When intensity is used as a point value, the resulting raster contains mean intensity per cell. Note that mean gives heights influenced by the vertical distribution of points
- stddev
- This computes the standard deviation of point values for each cell.
- variance
- This computes the variance of point values for each cell. Variance and derivatives use the biased estimator (n) [note that this might be subject to change].
- coeff_var
- This computes the coefficient of variance of point values for each cell. Coefficient of variance is given in percentage and defined as (stddev/mean)*100.
- median
- This computes the median of point values for each cell
- percentile
- pth (nth) percentile of points in cell
- skewness
- This is a skewness of point values in cell
- trimmean
- This is a trimmed mean of point values in cell. Trimmed mean also know as truncated mean is a mean computed after discarding values at the low end and at the high end. How many values to discard is given by the trim option in percent. In statistics the usual percentage of trimmed values ranges from 5 to 25 percent.
Filtering
Points falling outside the current computational region will be skipped. This includes points falling exactly on the southern region bound. To capture those adjust the region with:g.region s=s-0.000001
The zrange parameter may be used for filtering the input data by vertical extent. Example uses include filtering out extreme outliers and outliers on relatively flat terrain. This parameter can be also used for cutting the point cloud into vertical sections preparing it for further processing by separate sections, together as if it would be an imagery group (see i.group), or combined into a 3D raster using r.to.rast3. In for these last examples, it might actually be more advantageous to use r3.in.lidar module. The zrange parameter is especially powerful when used together with the base_raster parameter. The zrange is applied to Z values after the base_raster reduction.
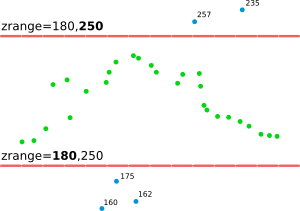
Figure: This is the principle of zrange filter. Points with the Z coordinate value below the lower value in the range (here 180) are filtered out (blue points) and same applies for points above higher value in the range (here 250). All other points are preserved (green points).
A LiDAR pulse can have multiple returns. The first return values can be used to obtain a digital surface model (DSM) where e.g. canopy cover is represented. The last return values can be used to obtain a digital terrain model (DTM) where e.g. the forest floor instead of canopy cover is represented. The return_filter option allows selecting one of first, mid, or last returns. Return number and number of returns in the pulse associated with each point are compared to determine if the point is first, mid, or last return.
LiDAR points often come as already classified into standardized classes. For example, class number 2 represents ground. For other classes see LAS format specification in references. The class_filter option allows selecting one or more classes using numbers (integers) separated by comma.
In varied terrain the user may find that min maps make for a good noise filter as most LIDAR noise is from premature hits. The min map may also be useful to find the underlying topography in a forested or urban environment if the cells are oversampled.
The user can use a combination of r.in.lidar output maps to create custom raster-based filters, for examplee, use r.mapcalc to create a mean-(2*stddev) map. (In this example the user may want to include a lower bound filter in r.mapcalc to remove highly variable points (small n) or run r.neighbors to smooth the stddev map before further use.)
Note that proper filtering of the input points in not only critical for the analysis itself but it can also speed up the processing.
Reduction to a base raster
For analysis of features on the terrain surface, especially vegetation it is advantageous to remove the influence of the terrain on heights because the height above the terrain is important (e.g. height of a tree) rather than height of the top of the tree above the see level. In this case, the base raster would be digital elevation model which can be one derived from the point cloud, or obtained in some other way. LiDAR data often come with precomputed DEMs (quality should be checked in this case) and there is often a DEM available for a given area (fit with the point cloud, especially vertical, and resolution should be checked).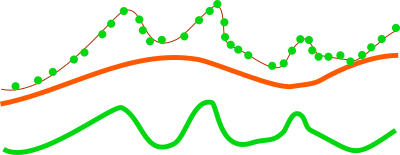
Figure: This is a profile of base raster (in orange) representing digital elevation model and selected points, e.g. first return, from point cloud (green dots). By default the points would create a digital surface model (thin brown line) but after reducing the Z coordinates using the base raster, the created surface is a derived from the height of points relative to the base raster.
Setting extent and resolution
Since the creation of raster maps depends on the computational region settings (extent and resolution), as default the current region extents and resolution are used for the import. When using the -e flag along with the resolution=value parameter, the region used for the new raster will be based the point cloud extent and the provided resolution. It is therefore recommended to first use the -s flag to get the extents of the LiDAR point cloud to be imported, then adjust the current region extent and resolution accordingly, and only then proceed with the actual import. Another option is to automatically set the region extents based on the LAS dataset itself (-e flag) along with the desired raster resolution. The best option is to know the point cloud extent ahead, e.g. from tiling scheme, and use it. See below for details.
Since the r.in.lidar generates a raster map through binning from the original LiDAR points, the target computational region extent and resolution have to be determined. A typical workflow would involve the examination of the LAS data's associated documentation or the scan of the LAS data file with r.in.lidar's -s (or -g) flag to find the input data's bounds.
Another option is to automatically set the region extents based on the LAS dataset extent (-e flag) along with the desired raster resolution using the resolution parameter.
Using the -s scan flag, the extent of the input data (and thus point density) is printed. To check this is recommended before performing the full import. The -g shell style flag prints the extent suitable as command line parameters for g.region.
A simpler option is to automatically set the region extents based on the LAS dataset (-e flag) along with the target raster resolution using the resolution parameter. Also here it is recommended to verify and optimize the resulting region settings with g.region prior to importing the dataset.
NOTES
Format and projection support
The typical file extensions for the LAS format are .las and .laz (compressed). The compressed LAS (.laz) format can be imported only if libLAS has been compiled with LASzip support. It is also recommended to compile libLAS with GDAL which is used to test if the LAS projection matches that of the GRASS location.LAS file import preparations
Note that the scanning (-s or -g flags) needs to iterate over the whole point cloud. This will take a long time for large datasets, so if the user knows the approximate extent of the dataset, for example because it dataset for one county or tiling scheme is available as vector polygons, it is much more advantageous to provide the extent information instead of retrieving it from the dataset. The same applies to the -e flag which also needs to perform scanning before the binning begins.Also note that the scanning does not apply any filters, so the extent determined by scanning can be theoretically bigger than the extent actively used during the binning. This behavior ensures that the newly created raster has always the same extent regardless the filters used. However, for most cases (considering the point cloud and the resolution used) there is no difference between the extent without filters applied and the extent if the filters would be applied.
Memory consumption
While the input file can be arbitrarily large, r.in.lidar will use a large amount of system memory (RAM) for large raster regions (> 10000x10000 pixels). If the module refuses to start complaining that there isn't enough memory, use the percent parameter to run the module in several passes. In addition using a less precise map format (CELL [integer] or FCELL [floating point]) will use less memory than a DCELL [double precision floating point] output map. For method=n, the CELL format is used automatically.
The mean and range methods will use average amount of memory (comparing to other methods). Methods such as n, min, max, and sum will use less memory, while stddev, variance, and coeff_var will use more.
The memory usage for regular statistics mentioned above is based solely on region (raster) size. However, the aggregate functions median, percentile, skewness and trimmean will use more memory and may not be appropriate for use with arbitrarily large input files without a small value for the percent option because unlike the other statistics memory use for these also depends on the number of data points.
The default map type=FCELL is intended as compromise between preserving data precision and limiting system resource consumption.
EXAMPLES
Simple example of binning of point from a LAS file into a newly created raster map in an existing location/mapset (using metric units):# set the computational region automatically, resol. for binning is 5m r.in.lidar -e -o input=points.las resolution=5 output=lidar_dem_mean g.region raster=lidar_dem_mean -p r.univar lidar_dem_mean
Finding suitable extent and resolution
Using the -s scan flag, the extent of the input data (and thus point density) is printed. To check this is recommended before performing the full import. The -g shell style flag prints the extent suitable as command line parameters for g.region.A simpler option is to automatically set the region extents based on the LAS dataset (-e flag) along with the target raster resolution using the resolution parameter. Also here it is recommended to verify and optimize the resulting region settings with g.region prior to importing the dataset.
For the output raster map, a suitable resolution can be found by dividing the number of input points by the area covered (this requires an iterative approach as outlined here):
# print LAS metadata (Number of Points)
r.in.lidar -p input=points.las
# Number of Point Records: 1287775
# scan for LAS points cloud extent
r.in.lidar -sg input=points.las output=dummy -o
# n=2193507.740000 s=2190053.450000 e=6070237.920000 w=6066629.860000 b=-3.600000 t=906.000000
# set computation region to this extent
g.region n=2193507.740000 s=2190053.450000 e=6070237.920000 w=6066629.860000 -p
# print resulting extent
g.region -p
# rows: 3454
# cols: 3608
# points_per_cell = n_points / (rows * cols)
# Here: 1287775 / (3454 * 3608) = 0.1033359 LiDAR points/raster cell
# As this is too low, we need to select a lower raster resolution
g.region res=5 -ap
# rows: 692
# cols: 723
# Now: 1287775 / (692 * 723) = 2.573923 LiDAR points/raster cell
# import as mean
r.in.lidar input=points.las output=lidar_dem_mean method=mean -o
# import as max
r.in.lidar input=points.las output=lidar_dem_max method=max -o
# import as p'th percentile of the values
r.in.lidar input=points.las output=lidar_dem_percentile_95 \
method=percentile pth=95 -o
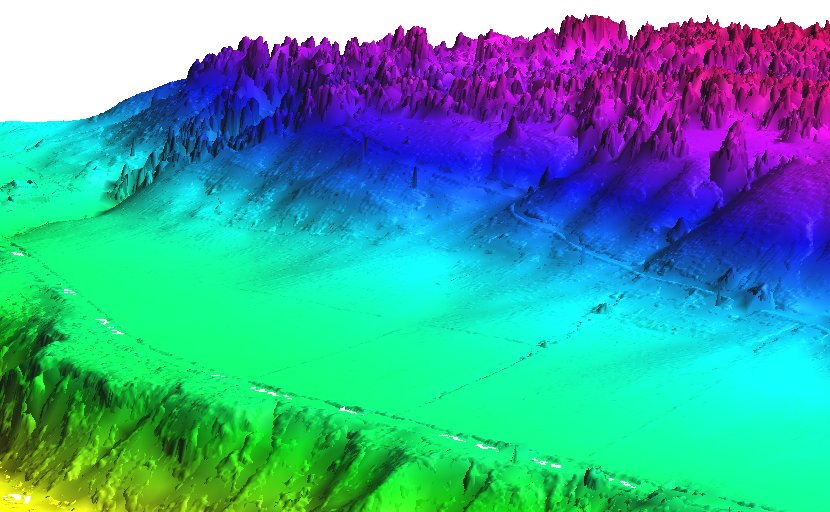
Mean value DEM in perspective view, imported from LAS file
Further hints: how to calculate number of LiDAR points/square meter:
g.region -e # Metric location: # points_per_sq_m = n_points / (ns_extent * ew_extent) # Lat/Lon location: # points_per_sq_m = n_points / (ns_extent * ew_extent*cos(lat) * (1852*60)^2)
Serpent Mound dataset
This example is analogous to the example used in the GRASS wiki page for importing LAS as raster DEM.The sample LAS data are in the file "Serpent Mound Model LAS Data.las", available at appliedimagery.com:
# print LAS file info
r.in.lidar -p input="Serpent Mound Model LAS Data.las"
# using v.in.lidar to create a new location
# create location with projection information of the LAS data
v.in.lidar -i input="Serpent Mound Model LAS Data.las" location=Serpent_Mound
# quit and restart GRASS in the newly created location "Serpent_Mound"
# scan the extents of the LAS data
r.in.lidar -sg input="Serpent Mound Model LAS Data.las"
# set the region to the extents of the LAS data, align to resolution
g.region n=4323641.57 s=4320942.61 w=289020.90 e=290106.02 res=1 -ap
# import as raster DEM
r.in.lidar input="Serpent Mound Model LAS Data.las" \
output=Serpent_Mound_Model_LAS_Data method=mean
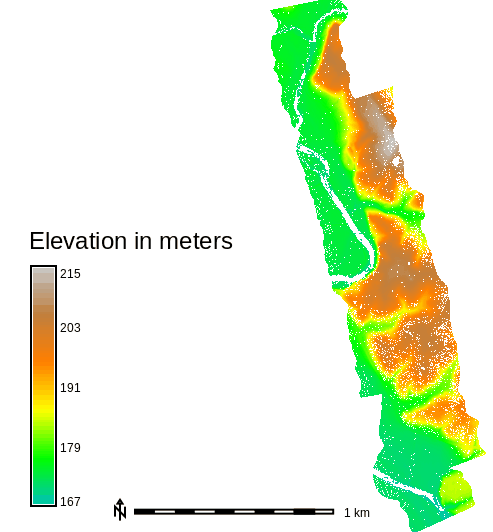
Figure: Elevation for the whole area of Serpent Mound dataset
Height above ground
The mean height above ground of the points can be computed for each raster cell (the ground elevation is given by the raster map elevation):g.region raster=elevation -p r.in.lidar input=points.las output=mean_height_above_ground base_raster=elevation method=mean
Multiple file input
The file option requres a file that contains a list of file names with the full path. For example, a list of files in the directory /home/user/data:points1.laz points2.laz points3.laz
/home/user/data/points1.laz /home/user/data/points2.laz /home/user/data/points3.laz
ls /home/user/data/*.laz > /home/user/data/filelist.txt
dir /b c:\users\user\data\*.laz > c:\users\user\data\filelist.txt
g.region raster=elevation -p r.in.lidar file=/home/user/data/filelist.txt output=mean_height_above_ground base_raster=elevation method=mean
import glob
import gscript
file_list_name = '/home/user/data/filelist.txt'
with open(, mode='w') as file_list:
for path in glob.iglob('/home/user/data/lidar/*.las'):
file_list.write(path + "\n")
gscript.run_command('r.in.lidar', file=file_list_name,
output='mean_height_above_ground',
base_raster='elevation' method='mean')
KNOWN ISSUES
- The "nan" value (as defined in C language) can leak into coeff_var raster maps. Cause is unknown. Possible work-around is: r.null setnull=nan or r.mapcalc 'no_nan = if(map == map, map, null())'.
- Only one method can be applied for a single run and multiple map output from a single run (e.g. method=string[,string,...] output=name[,name,...] or n=string mean=string) is no supported.
SEE ALSO
g.region, r.in.xyz, r.mapcalc, r.univar, v.in.lidar, r3.in.lidar, v.vect.statsv.lidar.correction, v.lidar.edgedetection, v.lidar.growing, v.outlier, v.surf.bspline
Trimmed mean (Truncated mean, Wikipedia article), OpenTopography (LiDAR point cloud repository)
REFERENCES
- V. Petras, A. Petrasova, J. Jeziorska, H. Mitasova (2016): Processing UAV and lidar point clouds in GRASS GIS. XXIII ISPRS Congress 2016 [ISPRS Archives, ResearchGate]
- ASPRS LAS format
- LAS library
- LAS library C API documentation
AUTHORS
Markus MetzVaclav Petras, NCSU GeoForAll Lab (base_raster option, documentation)
based on r.in.xyz by Hamish Bowman and Volker Wichmann
Last changed: $Date: 2016-08-22 19:07:22 -0700 (Mon, 22 Aug 2016) $
SOURCE CODE
Available at: r.in.lidar source code (history)
Note: A new GRASS GIS stable version has been released: GRASS GIS 7.6, available here.
Updated manual page: here
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2019 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.2.4svn Reference Manual