Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that has been discontinued. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.

NAME
v.perturb - Random location perturbations of vector points.KEYWORDS
vector, geometry, statistics, random, point pattern, level1SYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -b
- Do not build topology
- Advantageous when handling a large number of points
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Or data source for direct OGR access
- layer=string
- Layer number or name ('-1' for all layers)
- A single vector map can be connected to multiple database tables. This number determines which table to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: -1
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
- distribution=string
- Distribution of perturbation
- Options: uniform, normal
- Default: uniform
- parameters=float[,float,...] [required]
- Parameter(s) of distribution
- If the distribution is uniform, only one parameter, the maximum, is needed. For a normal distribution, two parameters, the mean and standard deviation, are required.
- minimum=float
- Minimum deviation in map units
- Default: 0.0
- seed=integer
- Seed for random number generation
- Default: 0
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
v.perturb reads a vector map of points and writes the same points but perturbs the eastings and northings by adding either a uniform or normal delta value. Perturbation means that a variating spatial deviation is added to the coordinates.NOTES
The uniform distribution is always centered about zero. The associated parameter is constrained to be positive and specifies the maximum of the distribution; the minimum is the negation of that parameter. Do perturb into a ring around the center, the minimum parameter can be used.Usually, the mean (first parameter) of the normal distribution is zero (i.e., the distribution is centered at zero). The standard deviation (second parameter) is naturally constrained to be positive.
Output vector points are not guaranteed to be contained within the current geographic region.
EXAMPLES
Random, uniformly distributed selection
To create a random, uniformly distributed selection of possible new points with a radius of 100,000 map units, use the following command:v.perturb input=comm_colleges output=uniform_perturb parameters=100000
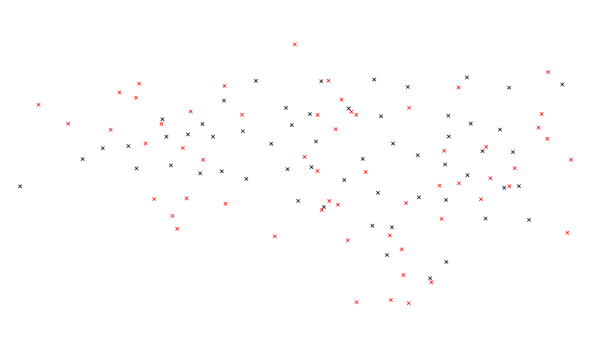
Figure: Map showing the actual community college points and uniformly random chosen points.
Normal distributed selection
For a normal distribution with a mean of 5000 and standard deviation of 2000, use the following command:v.perturb input=comm_colleges output=normal_perturb distribution=normal parameters=5000,2000

Figure: Map showing the actual community college points and normally random chosen and colored points. Notice that each point is closer to the original point.
Normal distributed selection with a minimum value
In order to include a minimum value of 500, use the following command:v.perturb input=comm_colleges output=min_perturb distribution=normal parameters=100000,1000 minimum=500
SEE ALSO
v.random, v.univarAUTHOR
James Darrell McCauleywhen he was at: Agricultural Engineering Purdue University
Random number generators originally written in FORTRAN by Wes Peterson and translated to C using f2c.
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.perturb source code (history)
Latest change: Monday Nov 18 20:15:32 2019 in commit: 1a1d107e4f6e1b846f9841c2c6fabf015c5f720d
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.9dev Reference Manual