
Note: A new GRASS GIS stable version has been released: GRASS GIS 7.6, available here.
Updated manual page: here
NAME
v.select - Selects features from vector map (A) by features from other vector map (B).KEYWORDS
vector, geometry, spatial querySYNOPSIS
v.select
v.select --helpv.select [-tcr] ainput=name [alayer=string] [atype=string[,string,...]] binput=name [blayer=string] [btype=string[,string,...]] output=name operator=string [relate=string] [--overwrite] [--help] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--ui]
Flags:
- -t
- Do not create attribute table
- -c
- Do not skip features without category
- -r
- Reverse selection
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- ainput=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Input vector map from which to select features (A)
- alayer=string
- Layer number (vector map A)
- Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: 1
- atype=string[,string,...]
- Feature type (vector map A)
- Input feature type
- Options: point, line, boundary, centroid, area
- Default: point,line,area
- binput=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Query vector map (B)
- blayer=string
- Layer number (vector map B)
- Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: 1
- btype=string[,string,...]
- Feature type (vector map B)
- Input feature type
- Options: point, line, boundary, centroid, area
- Default: point,line,area
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
- operator=string [required]
- Operator defines required relation between features
- A feature is written to output if the result of operation 'ainput operator binput' is true. An input feature is considered to be true, if category of given layer is defined.
- Options: overlap, equals, disjoint, intersects, touches, crosses, within, contains, overlaps, relate
- Default: overlap
- overlap: features partially or completely overlap
- equals: features are spatially equals (using GEOS)
- disjoint: features do not spatially intersect (using GEOS)
- intersects: features spatially intersect (using GEOS)
- touches: features spatially touches (using GEOS)
- crosses: features spatially crosses (using GEOS)
- within: feature A is completely inside feature B (using GEOS)
- contains: feature B is completely inside feature A (using GEOS)
- overlaps: features spatially overlap (using GEOS)
- relate: feature A is spatially related to feature B (using GEOS, requires 'relate' option)
- relate=string
- Intersection Matrix Pattern used for 'relate' operator
Table of contents
- DESCRIPTION
- NOTES
- EXAMPLES
- OVERLAP: features partially or completely overlap (using GRASS)
- OVERLAPS features spatially overlap (using GEOS)
- DISJOINT: features do not spatially intersect (using GEOS)
- EQUALS: features are spatially equals (using GEOS)
- INTERSECTS: features spatially intersect (using GEOS)
- TOUCHES: features spatially touches (using GEOS)
- CROSSES: features spatially crosses (using GEOS)
- WITHIN feature A is completely inside feature B (using GEOS)
- CONTAINS feature B is completely inside feature A (using GEOS)
- RELATE feature A is spatially related to feature B (using GEOS)
- Extraction of points falling into a polygon
- Extraction of lines overlapping with a polygon
- Extraction of areas overlapping with a line
- SEE ALSO
- AUTHORS
DESCRIPTION
v.select allows the user to select features from a vector map by features from another one.Supported operators (without GEOS; using GRASS' own algorithm):
- overlap - features partially or completely overlap
- equals - features are spatially equals
- disjoint - features do not spatially intersect
- intersects - features spatially intersect
- touches - features spatially touches
- crosses - features spatially crosses
- within - feature A is completely inside feature B
- contains - feature B is completely inside feature A
- overlaps - features spatially overlap
- relate - feature A is spatially related to feature B
NOTES
Only features with category numbers will be considered. If required the v.category module can be used to add them. Typically boundaries do not need to be given a category number, as an area's attributes are inherited from the centroid. Typically points, lines, and centroids will always want to have a cat number. E.g. take a road which separates two farms. It is ambiguous as to which farm an attribute that is attached to the road belongs to. The boundary only needs a cat number if it will hold its own attributes, such as road name or pavement form. A centroid in each paddock holds the information with respect to ownership, area, etc.EXAMPLES
Preparation of example data (North Carolina sample dataset):
# Create an grid for overlaying to ZIP code vector map
v.mkgrid map=boxgrid grid=10,10 position=coor \
coordinates=583600,201500 box=5000,5000
# set region to ZIP codes and boxgrid vector maps
g.region vector=zipcodes_wake,boxgrid -p res=100 -a
# enlarge region a bit for "white border" around map in monitor
g.region n=n+1000 s=s-1000 w=w-1000 e=e+1000 -p
d.mon wx0
OVERLAP: features partially or completely overlap (using GRASS)
Select grid boxes (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=boxgrid fill_color=85:130:176 v.select ainput=boxgrid binput=zipcodes_wake output=v_select_OVERLAP operator=overlap d.vect map=v_select_OVERLAP d.vect map=zipcodes_wake type=boundary color=50:50:50
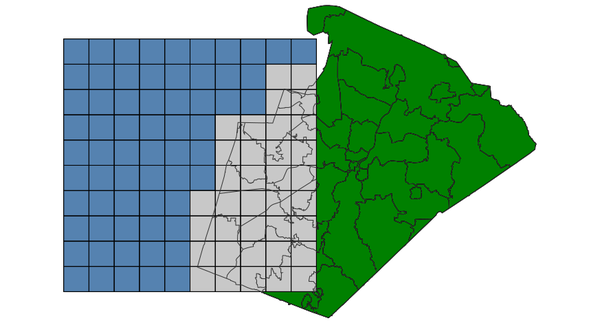
v.select with OVERLAP operator: selected grid boxes shown in grey
OVERLAPS features spatially overlap (using GEOS)
Select grid boxes (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=boxgrid fill_color=85:130:176 v.select ainput=boxgrid binput=zipcodes_wake output=v_select_OVERLAPS operator=overlaps d.vect map=v_select_OVERLAPS d.vect map=zipcodes_wake type=boundary color=50:50:50
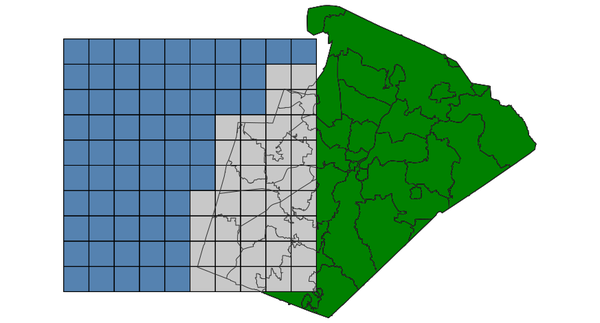
v.select with OVERLAPS operator: selected grid boxes shown in grey
DISJOINT: features do not spatially intersect (using GEOS)
Select grid boxes (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=boxgrid fill_color=85:130:176 v.select ainput=boxgrid binput=zipcodes_wake output=v_select_DISJOINT operator=disjoint d.vect map=v_select_DISJOINT d.vect map=zipcodes_wake type=boundary color=50:50:50
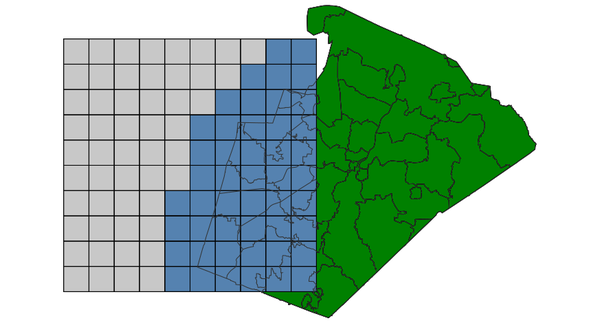
v.select with DISJOINT operator: selected grid boxes shown in grey
EQUALS: features are spatially equals (using GEOS)
Select zipcode polygon (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 v.extract input=zipcodes_wake where=ZIPCODE_ID=35 output=zipcodeID35 v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=zipcodeID35 output=v_select_EQUALS operator=equals d.vect map=v_select_EQUALS d.vect map=zipcodes_wake type=boundary color=50:50:50
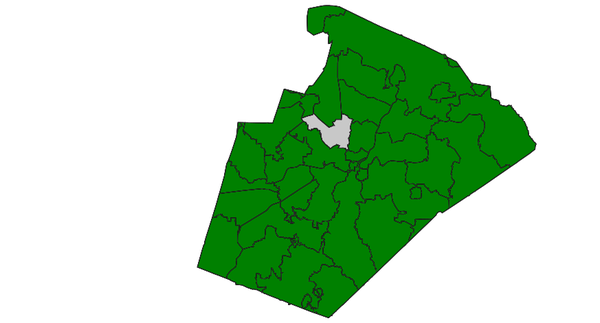
v.select with EQUALS operator: selected grid boxes shown in grey
INTERSECTS: features spatially intersect (using GEOS)
Select zipcode polygons (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=boxgrid fill_color=85:130:176 v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=boxgrid output=v_select_INTERSECTS operator=intersects d.vect map=v_select_INTERSECTS d.vect map=boxgrid type=boundary color=50:50:50
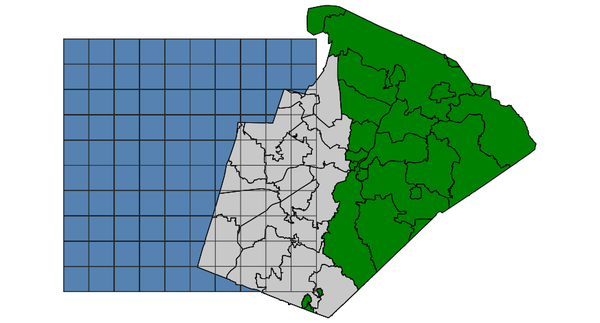
v.select with INTERSECTS operator: selected grid boxes shown in grey
TOUCHES: features spatially touches (using GEOS)
Select polygons (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=zipcodeID35 fill_color=85:130:176 v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=zipcodeID35 output=v_select_TOUCHES operator=touches d.vect map=v_select_TOUCHES d.vect map=zipcodes_wake type=boundary color=50:50:50
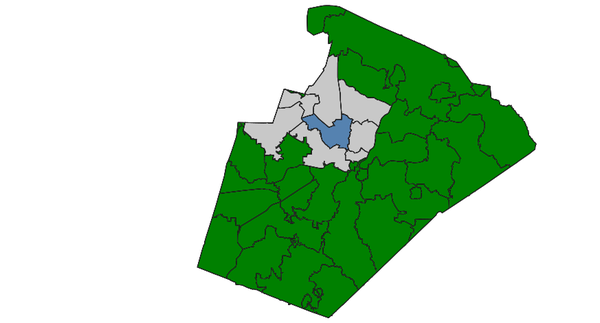
v.select with TOUCHES operator: selected polygons shown in grey (blue: input polygon)
CROSSES: features spatially crosses (using GEOS)
Select zipcode polygons by lines (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=busroute1 color=200:27:27 width=3 v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=busroute1 output=v_select_CROSSES operator=crosses d.vect map=v_select_CROSSES d.vect map=zipcodes_wake type=boundary color=50:50:50 d.vect map=busroute1 color=200:27:27 width=3
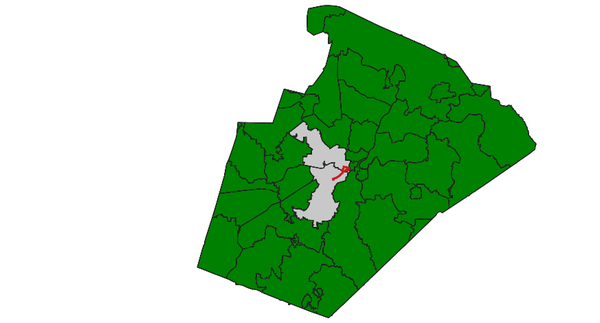
v.select with CROSSES operator: selected polygons shown in grey (red: input lines)
WITHIN feature A is completely inside feature B (using GEOS)
Select zipcode polygons (North Carolina sample dataset):d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0 d.vect map=boundary_county fill_color=85:130:176 v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=boundary_county output=v_select_WITHIN operator=within d.vect map=v_select_WITHIN
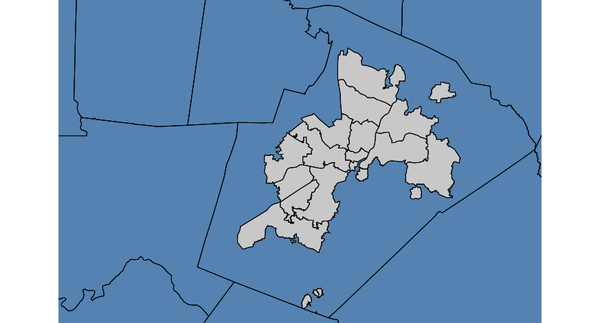
v.select with WITHIN operator: selected polygons shown in grey (blue: input polygons)
CONTAINS feature B is completely inside feature A (using GEOS)
Select zipcode polygon (North Carolina sample dataset):CONTAINS with polygons
d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0
d.vect map=zipcodeID35 fill_color=85:130:176
v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=zipcodeID35 \
output=v_select_CONTAINS_pol operator=contains
d.vect map=v_select_CONTAINS
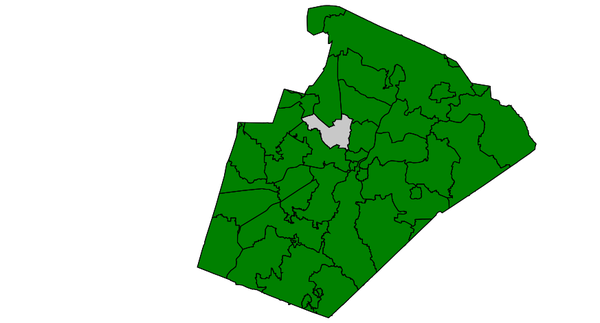
v.select with CONTAINS operator: selected polygon shown in grey (blue: input polygon, not visible)
CONTAINS with points
d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0
d.vect map=hospitals fill_color=195:31:31 icon=basic/cross3 size=10
v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=hospitals \
output=v_select_CONTAINS_pnts operator=contains
d.vect map=v_select_CONTAINS_pnts
d.vect map=hospitals fill_color=195:31:31 icon=basic/cross3 size=10
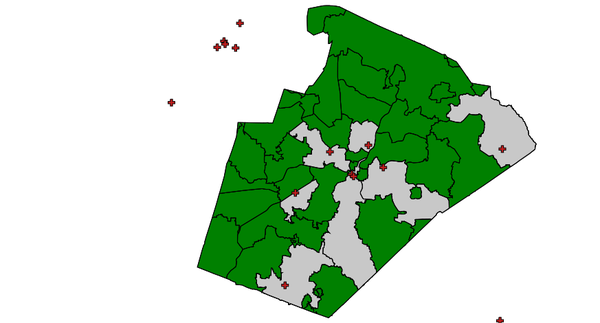
v.select with CONTAINS operator: selected polygons shown in grey (red: input points)
RELATE feature A is spatially related to feature B (using GEOS)
This operator additionally requires the relate parameter (in other GIS called 'ST_Relate'). This operator allows calculating the Dimensionally Extended nine-Intersection Model (DE-9IM). In the following one example: Select polygon with 'TOUCHES' operator (North Carolina sample dataset):
d.vect map=zipcodes_wake fill_color=0:128:0
d.vect map=zipcodeID35 fill_color=85:130:176
v.select ainput=zipcodeID35 binput=zipcodes_wake \
output=v_select_TOUCHES_relate operator=relate relate='T********'
d.vect map=v_select_TOUCHES
Extraction of points falling into a polygon
Extract fire stations (points) falling into urban area (polygon) - North Carolina data set (point in polygon test):
v.select ainput=firestations binput=urbanarea output=urban_firestations \
operator=overlap
Extraction of lines overlapping with a polygon
Extract railroad lines from zip code map overlapping with the urban area (line in polygon test):
v.select ainput=railroads binput=urbanarea \
output=railroads_in_urbanarea operator=overlap
Extraction of areas overlapping with a line
Extract those areas from zip code map which overlap with railroads (polygon on line test):# first add a tiny buffer around railroad lines: v.buffer input=railroads output=railroads_buf20m \ distance=20 v.select ainput=zipcodes_wake binput=railroads_buf20m \ output=zipcodes_wake_railroads operator=overlap
SEE ALSO
v.category, v.overlay, v.extract
GRASS SQL interface
GEOS - Geometry Engine, Open Source
AUTHORS
Radim BlazekGEOS support by Martin Landa, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
ZIP code examples by Carol X. Garzon-Lopez, Trento, Italy
Last changed: $Date: 2015-10-21 15:30:01 -0700 (Wed, 21 Oct 2015) $
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.select source code (history)
Note: A new GRASS GIS stable version has been released: GRASS GIS 7.6, available here.
Updated manual page: here
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2019 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.2.4svn Reference Manual